Data is at the heart of modern business analytics. To unlock actionable insights, it’s crucial to efficiently ingest and process data from various sources. That’s where data ingestion tools come into play—they ensure accurate, safe, and scalable data integration into your system.
With data piling up from countless sources, your choice of a data ingestion tool can either make or break your analytics process. To help you succeed, we’ve reviewed the 11 best data ingestion tools of 2024. This list will help you pick the right one to streamline your data ingestion and empower your data strategy.
11 Top Data Ingestion Tools
Let’s dive deeper into the detailed reviews of the 11 best data ingestion platforms to find the one that fits your needs.
1. Estuary Flow - Top Pick
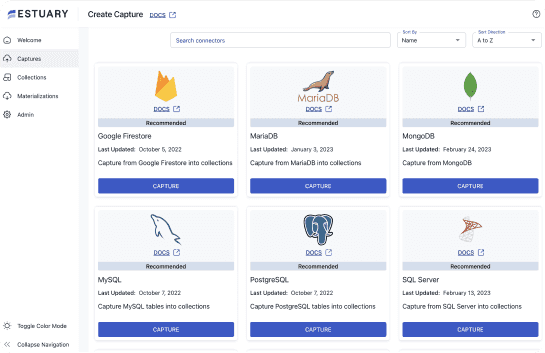
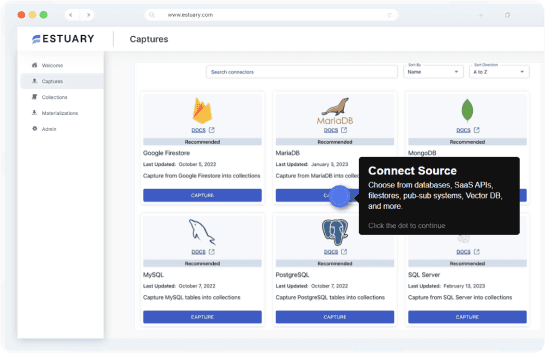
Estuary Flow is a real-time data ingestion tool that helps you collect, process, and analyze data from multiple sources in real time. It is a cloud-based SaaS platform that is easy to use and manage, even for non-technical users. It can capture data from a variety of sources in real time, including databases, cloud storage, and SaaS applications. This means that you can always have the latest data available for analysis.
Key Features
- Native Support for TypeScript: Estuary Flow offers native support for TypeScript to develop and maintain data pipelines.
- Flexible Data Destinations: It can load data into a variety of destinations, including databases, cloud storage, and data lakes.
- Highly Scalable & Reliable: It is designed to scale to meet your growing data integration and data orchestration needs. It is also highly reliable, with a 99.9% uptime guarantee.
- Schema inference: It converts unstructured data into a structured format which is helpful in stream processing scenarios where data comes in various formats.
- Streaming Micro-Transactions: Flow processes data using stable micro-transactions which guarantees that committed outcomes remain unaltered even in the event of crashes or machine failures.
- Open Protocol: It uses an open protocol for adding connectors which makes it easy to integrate with new data sources and sinks. This gives you the flexibility to build custom data pipelines that meet your specific needs.
- Dual-Nature Interface: Estuary Flow offers a dual-nature interface, with a user interface for non-technical users and a command-line interface for backend engineers. This makes it a good fit for teams of all sizes and skill levels.
- Powerful Transformations: Flow provides a variety of powerful data transformation capabilities, like filtering, sorting, aggregating, and joining. This lets you clean and prepare your data for analysis in any way you need.
Pricing
Estuary Flow offers Free, Cloud, and Enterprise plans. You can use the pricing calculator to estimate costs based on your specific needs and compare pricing with other tools like Fivetran and Confluent.
Pros & Cons
Pros | Cons |
| Fully managed platform | Initial learning curve because of its rich feature set |
| Real-time analytics capabilities | |
| Advanced data governance & security features | |
| GUI-based web application for easy pipeline management |
2. Apache Kafka
Apache Kafka is a powerhouse when it comes to data ingestion, particularly for streaming data. It's an open-source distributed event streaming platform known for handling high-throughput, fault-tolerant, and scalable data pipelines.
Key Features
- Fault Tolerance: It's built for resilience. Kafka replicates data across multiple brokers so even if a broker fails, your data remains safe and available.
- Real-time Data: With low latency, Kafka ensures data is ingested in real-time which makes it perfect for applications that require up-to-the-minute data.
- Connect API: To facilitate the data ingestion process from various origins, it offers multiple connectors for integrating with different data sources and sinks.
- Horizontal Scalability: Kafka is designed for high throughput and you can easily scale it horizontally by adding more brokers to accommodate growing data needs.
- Stream Processing: Kafka Streams API lets you process data within Kafka. This simplifies the data pipeline creation without the need for external stream processing tools.
- Publish-Subscribe Model: Kafka follows a pub/sub model that lets multiple producers send data to a topic and consumers can subscribe to those topics for real-time data ingestion.
Pros & Cons
Pros | Cons |
| Minimal data processing delays | Complex to set up & maintain |
| Comes with monitoring & management tools | |
| Retains data for a configurable period so you can replay or reprocess historical data | |
| Rich ecosystem provides seamless integration with a wide range of tools & platforms |
3. Amazon Kinesis Data Streams - Highly Scalable
Amazon Kinesis Data Streams is a powerful data ingestion tool within the AWS ecosystem. It's designed to efficiently ingest and process large volumes of real-time data from multiple sources. This tool is a go-to choice if you are looking to benefit from the potential of streaming data.
Key Features
- Data Retention Policies: You can set data retention policies to make sure that data is stored for the desired duration.
- Data Partitioning: It lets you partition data streams for parallel processing and efficient handling of high-throughput workloads.
- Data Sharding: It offers fine-grained control over data sharding that helps optimize data distribution and processing for specific use cases.
- Auto Scaling: The tool can automatically scale to accommodate increased data loads, reducing the need for manual adjustments and allowing for cost optimization.
- Integrations with AWS Services: Kinesis Data Streams seamlessly integrates with other AWS services like Lambda, Kinesis Data Firehose, and Kinesis Data Analytics.
- Real-time Data Streaming: Kinesis Data Streams is unmatched in real-time data ingestion which makes it ideal for applications that require immediate access to data, like IoT, social media, and clickstream data.
Pros & Cons
Pros | Cons |
| Highly scalable | Auto-scaling can cause unexpected costs if not closely monitored |
| Comes with integrated security features | |
| Can ingest data from multiple data sources | |
| Real-time metric data monitoring & analysis |
4. Apache NiFi - Most Secure
Apache NiFi is an advanced data ingestion tool designed to efficiently collect, transform, and transport data from various sources to destinations. It can handle a wide range of data types, including log data and unstructured data. This makes it a valuable choice for data engineers and organizations looking for a flexible and reliable solution.
Key Features
- Data Prioritization: You can set data prioritization rules to ensure critical data is processed and delivered first.
- Data Transformation: NiFi includes processors for data transformation that let you cleanse, enrich, and convert data as it flows through the system.
- Data Provenance: It provides detailed data lineage and auditing so you can trace the origin and transformation of data throughout the ingestion process.
- Flow-Based Data Integration: NiFi's unique flow-based user interface lets you design data flows graphically which makes it easy to construct, modify, and visualize data pipelines.
- Dynamic Routing: NiFi offers dynamic routing based on data attributes which allows for conditional branching, filtering, and redirection of data to ensure data is delivered to the right destination.
- Security & Access Control: NiFi has advanced security features, including SSL encryption, user authentication, and role-based access control, which make sure that data remains secure during transport.
Pros & Cons
Pros | Cons |
| Extensive processor library | Complex data flows can become challenging to manage |
| Vibrant & active community | |
| Offers real-time monitoring & statistics | |
| Includes data recovery features in case of system failures |
5. Talend - Ideal For Complex Data Transformations
Talend is another worthy data integration and transformation platform on our list. It's a leading choice for organizations looking to streamline the process of collecting, processing, and moving data from various sources to their data warehouses or analytics systems.
Key Features
- Data Quality & Profiling: It includes built-in data quality tools and profiling capabilities to cleanse and enrich data as it's ingested.
- Data Masking: You can apply data masking techniques during data ingestion to protect sensitive information and comply with data privacy regulations.
- Automated Data Pipelines: Talend provides tools for building and automating complex data pipelines which reduces manual work and the risk of errors.
- Data Governance: The tool provides features for data lineage, impact analysis, and user access control to ensure data remains secure and compliant.
- Unified Data Integration: Talend offers a unified platform for data ingestion to connect and extract data from various sources, both structured and unstructured.
- Rich Ecosystem: Talend offers a vast ecosystem of connectors that lets you integrate with a wide range of data sources, data warehouses, and cloud platforms.
Pros & Cons
Pros | Cons |
| Data enrichment capabilities | Costly enterprise edition |
| User-friendly, drag-and-drop interface | |
| Offers both open-source & commercial versions | |
| Strong user community & extensive documentation |
6. Airbyte - Largest Catalog Of Connectors
Airbyte is a dynamic data ingestion tool that simplifies the process of collecting, transforming, and moving data from a multitude of sources to your chosen destination, like data warehouses, data lakes, or databases. It has gained rapid recognition lately for its ease of use and advanced capabilities.
Key Features
- Open-Source & Extensible: Airbyte is an open-source platform that makes it highly customizable and extensible.
- Incremental Data Sync: Airbyte performs incremental data sync to reduce the processing load and speed up data ingestion.
- Real-time Data Replication: Airbyte supports real-time data replication that lets you access and analyze fresh data for making informed decisions.
- Data Observability: The tool provides comprehensive data observability for monitoring data flows, tracking errors, and ensuring data quality in real time.
- Connector Library: It boasts a rich library of 300+ connectors for a wide range of data sources and the community actively contributes to expanding its capabilities.
- Schema Mapping: The platform includes schema mapping which allows you to transform and map data to meet the destination data store requirements.
- Serverless Deployment: You can opt for serverless deployment which reduces infrastructure management overhead, scaling resources automatically as needed.
Pros & Cons
Pros | Cons |
| Highly secure | May fall short when it comes to handling complex data transformations |
| Cost-effective solution | |
| User-friendly interface & easy setup process |
7. Integrate.io - Easy To Implement
Integrate.io is an advanced data integration platform designed for efficient and hassle-free data ingestion. It is highly valued in the data management world as it simplifies collecting and moving data from various sources to data warehouses.
Key Features
- Real-time Data Sync: It supports real-time data synchronization for up-to-the-minute updates in your data warehouse.
- Monitoring & Logging: Robust monitoring and logging give you real-time visibility into data flows and help track the data ingestion process.
- Customization & Automation: You can automate repetitive data ingestion tasks and create custom workflows to suit your specific business requirements.
- Extensive Connector Library: Integrate.io offers a vast array of pre-built connectors that simplify data import from databases, cloud storage, and SaaS applications.
- Data Deduplication: Integrate.io offers data deduplication capabilities to prevent redundant data from entering the data warehouse. This helps maintain a clean and efficient data repository.
Pros & Cons
Pros | Cons |
| Cost-effective | New users might feel overwhelmed by too many customization options |
| Extensive documentation available | |
| Responsive & knowledgeable customer support team | |
| Easily integrates with popular Business Intelligence (BI) tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Looker |
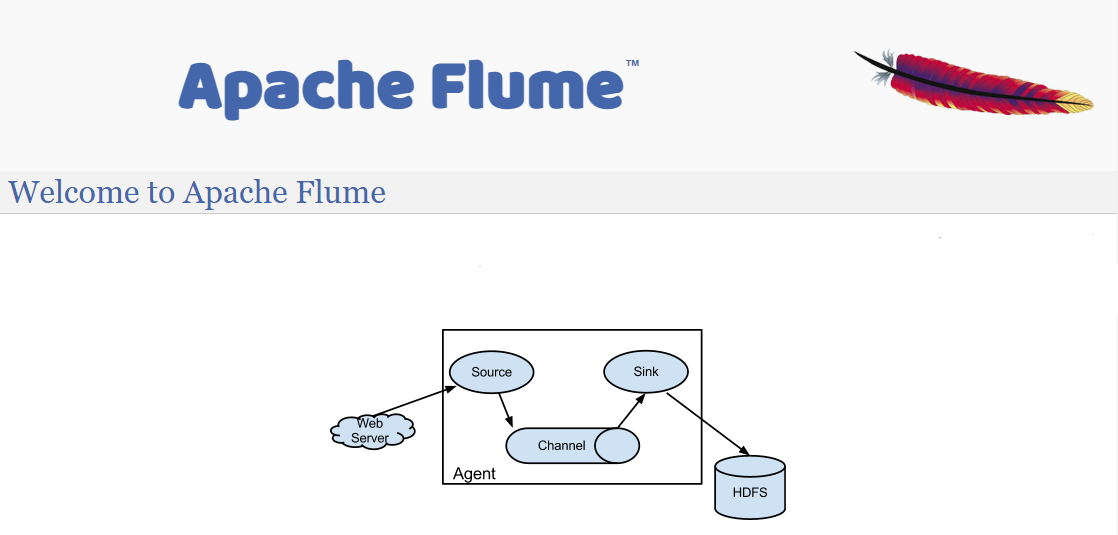
8. Apache Flume - Most Reliable
Apache Flume is a robust data ingestion tool designed for efficiently collecting, aggregating, and transporting large volumes of log and event data from various sources to storage systems, including the Hadoop distributed file system.
Key Features
- Scalability: The tool can add more data collection agents or adjust the configuration to suit growing requirements.
- Data Filtering & Transformation: You can apply filters and transformations to the data as it flows through the system.
- Reliable Data Transfer: Flume provides reliable data transfer through mechanisms like transactional guarantees which ensure that data is not lost during transport.
- Fault Tolerance: Flume supports data replication and automatic failover to ensure the continuous operation of data ingestion, even in the face of hardware or network failures.
- Data Collection Agents: Flume uses a distributed architecture that deploys multiple data collection agents across your network to efficiently gather data from numerous sources.
- Extensible: It offers a pluggable architecture with various sources, sinks, and channels, that lets you create custom plugins to accommodate unique data sources or destinations.
Pros & Cons
Pros | Cons |
| Cost-effective solution | Configuration can be complex & time-consuming |
| Integrates well with the Hadoop ecosystem | |
| Built-in mechanisms for data reliability & fault tolerance |
9. StreamSets - Ideal For Hybrid Environments
StreamSets is a versatile data ingestion tool that stands out with its focus on data flow management and real-time data processing. With its unique set of features and capabilities, StreamSets offers a level of control and adaptability that truly sets it apart.
Key Features
- Data Drift Handling: It detects changes in data schemas and handles data drift effectively.
- Dataflow Control: StreamSets provides a user-friendly, visual interface for designing dataflows.
- Change Data Capture (CDC): StreamSets supports CDC mechanisms that reduce processing overhead and improve efficiency.
- Data Versioning: You can keep track of different versions of data which is helpful in auditing and maintaining historical data for analysis.
- Real-time Monitoring: With real-time dashboard monitoring, you can keep an eye on data flows and spot and resolve issues as they arise.
- Built-in Data Quality: The tool includes built-in data quality checks that let you define data quality rules and automatically filter out erroneous data.
Pros & Cons
Pros | Cons |
| High data drift resilience | Limited built-in transformations |
| Enterprise-grade security | |
| Easy to build complex data pipelines | |
| Can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud |
10. Matillion - Best For Data Reliability
Matillion is an advanced data ingestion tool that excels in ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes. It's designed for organizations looking to seamlessly collect and prepare data from a variety of sources before loading it into their data warehouses or cloud storage.
Key Features
- Dynamic Scaling: It scales dynamically to handle data growth.
- Pre-built Connectors: The tool comes with a library of pre-built connectors for various data sources.
- Orchestration: Matillion provides orchestration capabilities to manage complex data pipelines and ensure smooth data flows.
- Advanced Security: Matillion prioritizes data security with features like encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry standards.
- Native Cloud Integration: Matillion provides optimal performance in cloud data warehouses like Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, and Snowflake.
- Codeless ETL: Matillion's code-free ETL design is user-friendly which makes it accessible to data engineers and analysts without extensive coding knowledge.
- Data Transformation: It offers a rich set of data transformation features for cleansing, enriching, and structuring data to meet the requirements of your analytics or reporting.
Pros & Cons
Pros | Cons |
| Rapid deployment | May not be the ideal choice for on-premises data infrastructure |
| Codeless ETL design | |
| Optimized for cloud data warehouses | |
| Scales dynamically to handle data growth |
11. Fluentd - Most Flexible
Fluentd is a key player in the data ingestion landscape. It is a powerful and flexible open-source data ingestion tool designed for collecting, parsing, and forwarding logs and other data from multiple sources to various destinations.
Key Features
- Multi-Source Ingestion: It's versatile in handling data from various sources, including files, sockets, and HTTP endpoints.
- Data Parsing: Fluentd can parse and structure data to transform raw data into structured information for further analysis.
- Load Balancing: Fluentd offers load-balancing capabilities to evenly distribute data across multiple destinations or data processing nodes.
- Plugin Ecosystem: With a rich plugin ecosystem, it's highly extensible. A wide array of community-contributed plugins further enhance its functionality.
- Log Forwarding: Fluentd is highly proficient in log collection and forwarding and streamlines the gathering of log data from applications, servers, and more.
- Built-in Reliability: It incorporates features like buffering and failover to ensure data reliability even in cases of network interruptions or destination unavailability.
Pros & Cons
Pros | Cons |
| Extensive plugin ecosystem | Documentation can be somewhat varied in quality and detail |
| Advanced, built-in reliability features | |
| Consume minimal system resources |
How To Pick The Right Data Ingestion Tool: 8 Factors To Consider
Choosing the right data ingestion tool is pivotal for a successful data strategy. Here are the major factors you should consider when making this critical decision:
Assess Data Volume & Velocity
Start by understanding the scale of your data. Analyze the volume (how much data you'll be handling) and velocity (how quickly data is generated or updated). Different tools are designed to handle varying data loads. Ensure the tool you choose can accommodate your data size and speed requirements.
Consider Data Source Compatibility
Identify the sources of your data. It could be databases, APIs, log files, or other systems. Ensure the data ingestion tool is compatible with the data sources you are working with. Compatibility issues can cause data loss or integration challenges.
Evaluate Scalability Requirements
Assess whether your data ingestion needs are likely to grow over time. Choose a tool that can scale with your data volume and velocity requirements. Scalability is crucial for accommodating future growth without major disruptions.
Analyze Cost & Licensing
Consider the total cost of ownership which includes both upfront costs and ongoing expenses. Compare the pricing models and licensing options of different data ingestion tools. Look out for any hidden costs like maintenance and support fees.
Check Integration With Existing Systems
Ensure that the chosen data ingestion tool can seamlessly integrate with your existing data infrastructure, including databases, analytics platforms, and other tools. Compatibility and ease of integration are important to prevent disruptions in your data pipeline.
Assess Real-Time Vs. Batch Processing Needs
Determine whether your data needs to be processed in real-time or if batch processing is sufficient. Some tools excel in real-time data ingestion while others are better suited for batch processing. Choose the one that aligns with your specific use cases.
Consider Cloud vs. On-Premises Deployment
Decide whether you want to deploy your data ingestion tool in the cloud or on-premises. Cloud-based solutions offer scalability and flexibility while on-premises solutions provide more control over data security and compliance. Make this decision based on your organization's requirements and resources.
Evaluate Community & Vendor Support
The availability of a strong user community and vendor support is vital. A thriving user community can provide valuable insights, troubleshooting tips, and best practices. Vendor support ensures you have assistance when encountering issues. Consider the level of support and documentation provided by the tool's vendor.
Conclusion
All data ingestion tools we've explored offer unique strengths and features. Some excel in real-time processing, while others are masters of batch data ingestion. Some are agile in the cloud, while others stand sturdy on-premises.
Remember, the best tool is the one that aligns with your needs. It should fit your budget, integrate seamlessly with existing systems, and be supported by a strong community or vendor.
Estuary Flow stands out as a reliable data ingestion tool that checks all the right boxes. It is a fully managed platform that is cost-effective and user-friendly, supporting various data sources. Estuary Flow's extensibility ensures easy connector additions and it offers real-time analytics for rapid event responses.
Explore Flow’s features by signing up for free. You can also reach out to our team for more information.
Frequently Asked Questions About Data Ingestion Tools
We know that choosing the right tool for data ingestion is a crucial part of streamlining your data workflows. That's why it's important to have all your questions answered and your concerns sorted out. Let’s take a look at some of these queries so you can confidently make a choice that's a perfect fit for your needs.
What are the types of data ingestion tools?
There are several types of data ingestion tools, including:
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) Tools: ETL tools extract data from source systems, transform it into a suitable format, and load it into a destination database.
- Log Shippers: Designed for streaming and analyzing log data, tools like Fluentd and Logstash collect and forward log files to a central repository.
- Message Queues: Platforms like Apache Kafka, Gazette, and RabbitMQ enable real-time data streaming and event-driven data ingestion.
- API Integrators: Tools like Zapier and Integromat connect applications and services by automating data transfers through APIs.
- Data Import APIs: Services like Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage allow users to import data directly into cloud-based storage systems.
What security measures should be in place when using data ingestion tools?
When using data ingestion tools, several critical security measures should be used to protect sensitive data:
- Employ end-to-end encryption to protect data during transmission and at rest.
- Implement strong access controls to ensure only authorized users can access and modify data.
- Validate incoming data to prevent malicious input or injection attacks.
- Continuously monitor tool activities and maintain detailed logs for threat detection and forensic analysis.
- Sensitive information should be masked or redacted to protect privacy.
- Regularly update the tool to address security vulnerabilities.
- Create backups to ensure data can be restored in case of data loss or breaches.
- Educate users on best practices to reduce human error.
- Secure the network infrastructure to prevent unauthorized access to the data ingestion tool.
What types of data sources can data ingestion tools support?
Data ingestion tools can support various data sources, including:
- Structured Databases (SQL and NoSQL databases)
- Unstructured Data (logs, text files)
- Cloud Services (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud)
- Streaming Data (IoT devices, social media feeds)
- External APIs (web services, REST, SOAP)
- Legacy Applications
- Web Scraping
- File Systems (local and network-based)
- Message Queues (Kafka, RabbitMQ)
- Data Lakes and Data Warehouses
- Content Management Systems (CMS)
- Social Media Platforms (Twitter, Facebook)
- Sensor Data
- Mobile Applications
- Email Servers
What are the common challenges when implementing data ingestion processes?
These are the major challenges that you can come across when implementing data ingestion processes:
- Ensuring accuracy and consistency of incoming data.
- Handling large data volumes while maintaining performance.
- Integrating data from various sources with differing formats.
- Protecting data during ingestion and ensuring compliance.
- Detecting errors and bottlenecks in data pipelines.
- Managing data ingestion speed to meet real-time or near-real-time requirements.
- Preventing or managing duplicate data entries in the ingestion process.

Author
Popular Articles