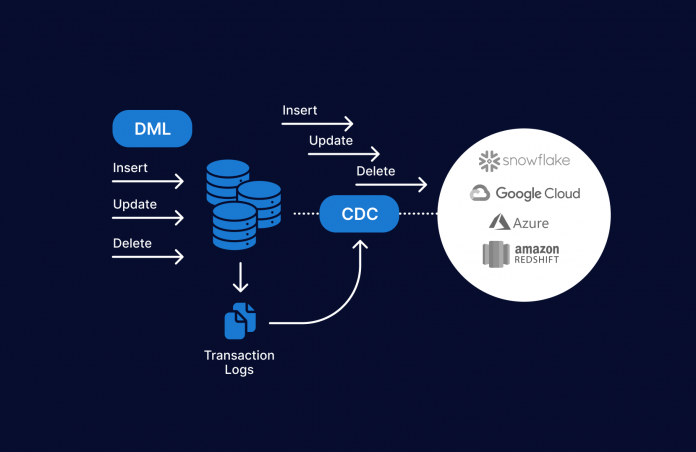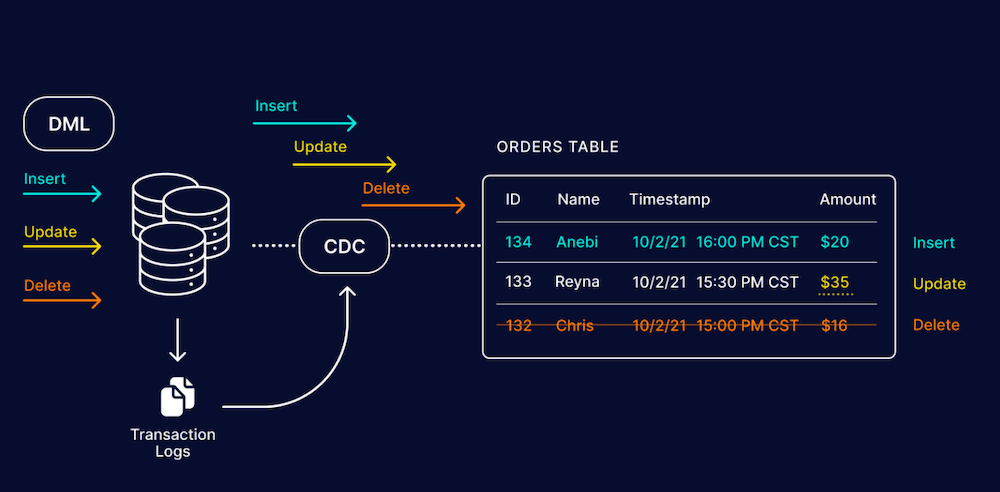
Real-time data is changing the way organizations manage and synchronize their data. As a crucial element of modern real-time data architectures, CDC replication enables analytics, synchronization, and enhanced data warehousing of real-time data.
This powerful technique is instrumental in modern data architectures as it ensures that data stays up-to-date and accessible in real time. With data volumes continuously growing, the need for real-time processing becomes paramount, making Change Data Capture replication the ideal solution.
But what exactly is it and how is it done? This is what we will be answering in this article. We’ll explain the significance of CDC replication and shed light on its various use cases. We'll also talk about different approaches and processes involved and share best practices for implementing CDC replication.
By the end of this guide, you'll understand CDC replication and its capacity better to greatly enhance your organization's data management and analytics.
What Is CDC Replication? A Detailed Overview
Let’s start by talking about what CDC replication is and how it can benefit organizations, particularly those using SQL databases like Postgres, MySQL, and SQL Server. Simply put, it is a technique that addresses the challenges of modern data architectures by efficiently capturing and processing data changes as they occur.
As organizations increasingly rely on real-time data to drive their decision-making and operations, CDC replication has emerged as a key enabler of this shift. By focusing on the incremental replication of data changes, Change Data Capture reduces the strain on source systems, enhances data processing performance, and ensures that target systems have access to the most current and accurate information.
The concept of CDC replication builds on the foundation of traditional ETL processes but with a focus on agility and responsiveness. As a result, organizations are increasingly adopting CDC replication to stay competitive in today's data-driven landscape.
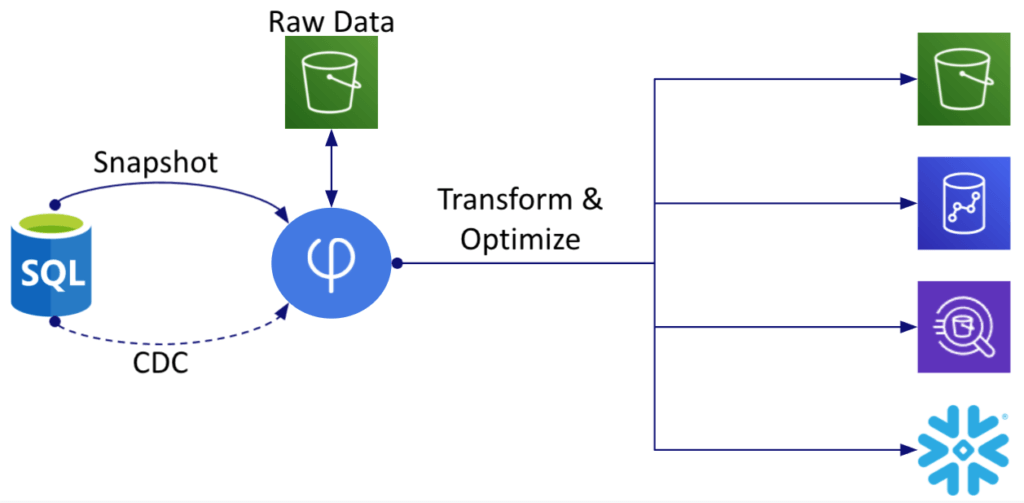
There are many fully-managed as well as self-managed platforms available these days to quickly set up Change Data Capture-CDC replication. One such solution that helps businesses harness the power of CDC replication is our DataOps platform, Estuary Flow. Flow provides a comprehensive platform for managing and optimizing your data pipelines, making it easier than ever to adopt and benefit from CDC replication.
Now that we have an understanding of CDC replication, let's see how it fares against traditional ETL.
How CDC Replication Differs From Traditional ETL?
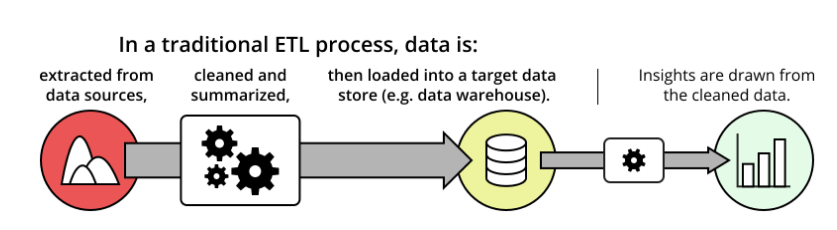
Traditional ETL processes extract all data from the source database, transform it, and load it into a target system.
Change Data Capture is employed to enhance the performance of an ETL pipeline but it is limited to the "Extract" stage of ETL. CDC not only saves time and resources but also makes the entire replication process more efficient and effective. CDC replication also supports instantaneous data processing, ensuring that target systems have the data available for analysis and decision-making.
As a result, CDC replication has become an important component of modern data pipelines, especially streaming ETL pipelines, providing businesses with the agility and responsiveness they need to succeed in today's data-driven world.
4 Popular CDC Replication Use Cases
CDC replication offers numerous use cases that can benefit companies across various industries. From real-time analytics and data synchronization to data warehousing and auditing compliance, CDC replication provides the tools necessary to make informed decisions based on the most current information available.
By staying on top of data changes, businesses can maintain a strong compliance posture and ensure high data integrity, making Change Data Capture replication an indispensable part of any modern data strategy.
Let’s discuss the 4 most common use cases of CDC replication.
I. Real-Time Analytics
With CDC replication, businesses can analyze and act on data as it changes. With this, they gain insights into market trends, customer behaviors, and operational performance. This leads to better-informed decision-making which leads to enhanced operations.
Real-time insights from CDC replication also allow organizations to act proactively to address potential issues before they escalate and seize opportunities as they arise. This responsiveness is essential for maintaining a competitive edge in today's dynamic business landscape.
II. Data Synchronization
Data synchronization is necessary for maintaining consistency across systems such as a database, data lake, and data warehouse. In this regard, Change Data Capture replication plays a vital role by rapidly capturing and sharing data changes, ensuring every system has access to the latest information.
By reducing data discrepancies and improving data quality, CDC replication helps businesses streamline their workflows and enhance collaboration between teams. This synchronization capability is particularly valuable in modern, distributed architectures, where data consistency is critical for success.
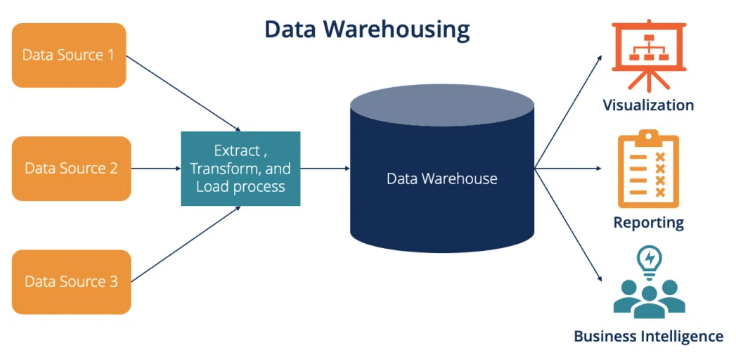
III. Data Warehousing
Data warehousing involves storing and managing large volumes of structured and semi-structured data for analysis and reporting purposes. CDC replication plays a significant part in populating and updating data warehouses with real-time and streaming data as it incrementally captures data changes and integrates them into the data warehouse.
Also, CDC replication helps companies save resources by avoiding the need for full data extractions and reducing the storage requirements of historical data.
IV. Auditing And Compliance
Today, there are more data auditing and data compliance requirements than ever before. CDC replication can help in this aspect as well. It provides a comprehensive audit trail that supports data governance and regulatory compliance efforts. This ensures businesses can demonstrate accountability and transparency in their data management practices.
In addition to meeting regulatory requirements, CDC replication's auditing capabilities help to identify and address data quality issues, maintain high data integrity, and improve overall data reliability.
By leveraging CDC replication, businesses can strengthen their compliance posture and ensure they are prepared for any audits or regulatory inquiries.
Now that we are familiar with the use cases, let’s take a look at CDC replication approaches.
Understanding The 3 CDC Replication Approaches For Efficient & Accurate Data Management
CDC can be implemented using 3 different replication approaches, each offering its distinct advantages and trade-offs. Let’s discuss each of these 3 and see how they can help businesses achieve efficient and accurate data management.
Log-Based CDC Replication
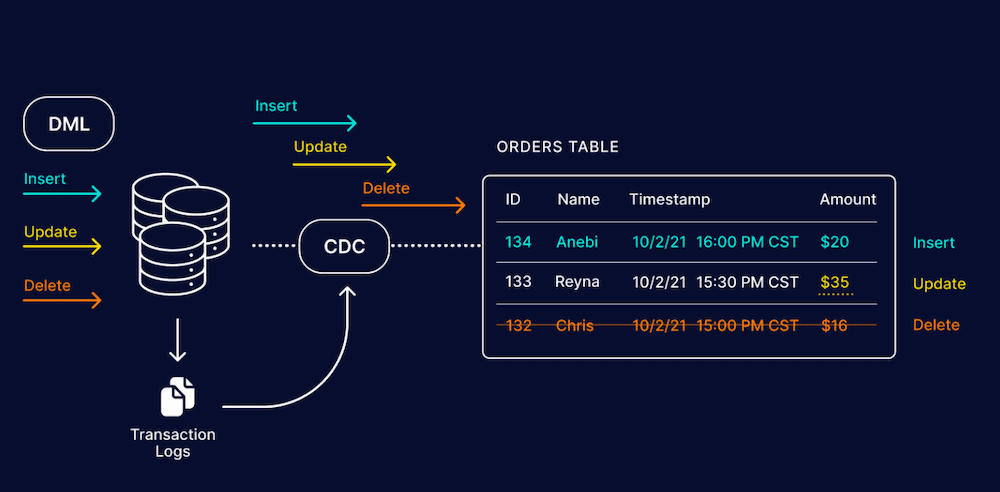
Log-based CDC replication is a highly efficient approach that monitors database transaction logs to identify and capture data changes. By directly accessing these logs, this method provides a minimally invasive solution that avoids placing additional load on the source system.
Key advantages of log-based CDC replication include:
- High accuracy and performance
- Minimal impact on the source system
- No need to modify source system tables
Log-based CDC replication is particularly well-suited for businesses with large-scale databases or those that require instantaneous data replication. Its non-intrusive nature ensures system stability while offering impressive performance.
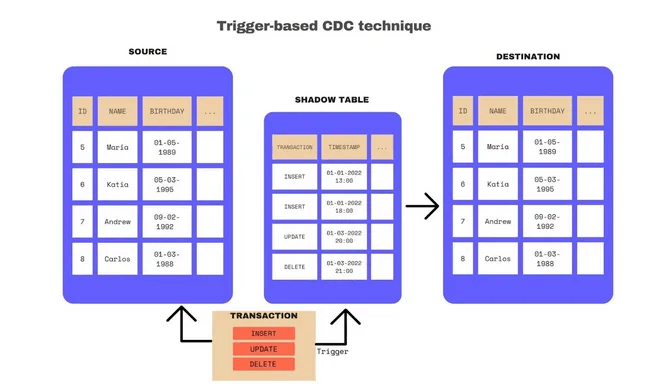
Trigger-Based CDC Replication
Trigger-based CDC replication employs database triggers placed on the source system's tables to detect and capture data changes.
Although this method requires modifications to the source system, it can be useful in certain scenarios, such as when a database transaction log is unavailable or when more control over data capture is required.
Major aspects of trigger-based CDC replication include:
- Fine-grained control over data capture
- Requires changes to source system tables
- Suitable for systems without accessible transaction logs
Despite its invasive nature, trigger-based CDC replication offers more control over data capture. This makes it a viable choice for organizations with specific data management requirements or those dealing with systems lacking accessible transaction logs.
Polling-Based CDC Replication
Polling-based CDC replication involves periodically querying the source system to identify data changes. The frequency of polling depends on the specific implementation but it typically ranges from a few seconds to several minutes. During each poll, the replication system checks for any new or modified data since the last poll.
While this approach is less efficient than log-based or trigger-based CDC replication, it can be useful when other options are not viable or when change frequency is low. In some legacy systems, it may not be possible to implement log-based or trigger-based replication. In such cases, polling-based replication may be the only viable option.
After having a detailed understanding of different Change Data Capture methods, let’s now discuss the steps involved in the actual process. By having a clear understanding of each stage, businesses can gain insights into the detection, processing, and integration of data changes into their target systems
3 Critical Steps Involved In The CDC Replication Process
The CDC replication process involves several key steps. Let’s see what they are:
Initial Snapshot
When you begin the CDC replication process, the first thing you need to do is create an initial snapshot of the source system's data. This snapshot captures the current state of the data in the source system and serves as a starting point for future tracking of changes.
The initial snapshot is essentially a snapshot of the source system's data at a particular point in time. Once this snapshot is taken, it's loaded into the target system, which is where the replicated data will reside.
The purpose of this initial snapshot is to establish a baseline for the replication process. Without it, the CDC replication process wouldn't know where to start tracking changes. The snapshot serves as a reference point for comparing the source system's data with the replicated data in the target system.
Once the initial snapshot is loaded into the target system, the CDC replication process can begin tracking changes in the source system's data to replicate data. It's important to note that the initial snapshot is not a one-time thing. Depending on how frequently data changes in the source system, you may need to take periodic snapshots to ensure that your replicated data stays up-to-date.
Capturing Change Events
After taking the initial snapshot of the source system's data, the next step in the CDC replication process is capturing change events. This step is important since it allows for continuous monitoring of the source system for any changes that occur.
There are several ways to capture change events which we have discussed earlier i.e. log-based, trigger-based, and polling-based CDC replication.
Regardless of the approach you choose, efficient change event capture is essential for maintaining data consistency and ensuring that the target system stays up-to-date with the latest changes in the source system.
If changes aren't captured quickly and accurately, the replicated data can quickly become out-of-date which defeats the purpose of the CDC replication process.
By continuously monitoring the source system for changes and capturing those changes efficiently, the CDC replication process ensures that the target system always reflects the latest state of the source system's data.
Transforming & Loading Changes
This step involves converting the captured changes into a format that can be understood by the target system and then applying them to the replicated data. It’s how you incorporate CDC into a complete ETL pipeline.
The transformation process can include several steps which mainly depend on the specific needs of the target system. For instance, you might need to map data from the source system to a different schema in the target system or convert data types to match the target system's requirements.
Once the changes have been transformed, they're loaded into the target system. This can be done in several ways, including.
- Batch processing is where changes are loaded in batches at regular intervals.
- Continuous loading is where changes are applied in real time as they're captured from the source system.
Once the changes are transformed and loaded into the target system, the CDC replication process is complete. The replicated data in the target system should now be up-to-date with the latest changes in the source system.
Now that we know how CDC replication actually works, let’s get familiarized with the best practices for implementing it to leverage its advantages to the fullest.
5 Best Practices For Implementing CDC Replication To Maximize Benefits
When deploying CDC replication, it is important to adhere to best practices that ensure optimal performance, data consistency, and system stability. This not only maximizes the benefits of CDC replication but also minimizes the risks associated with data replication and synchronization. Let’s discuss them in greater detail:
Choosing The Right CDC Replication Approach
Selecting the best CDC replication approach is essential considering your business. By selecting the appropriate method, you will effectively capture and propagate data changes in near-real-time, keeping all systems up-to-date.
Some factors to consider when choosing a method include:
- Integration with existing systems
- Support and community resources
- Database size and change frequency
- Flexibility to accommodate future growth
When assessing these factors, also consider the expertise and skill set of your team, as well as your organization's budget and resource constraints. Once you have carefully considered these factors, select the most appropriate CDC replication approach based on your needs. Regularly reevaluate your choice as advancements in Change Data Capture technology may require a shift to a different method.
In this context, it is important to consider various CDC replication tools and platforms, such as Airbyte, Fivetran, and Estuary. For a comprehensive comparison of these tools, refer to our guide on Airbyte vs Fivetran vs Estuary.
Ensuring Data Consistency & Integrity
Maintaining data consistency and integrity not only ensures that the data being replicated is accurate and reliable but also protects the integrity of the target system. To achieve data consistency and integrity, establish a robust data governance framework that includes policies, processes, and best practices for managing data assets.
Some factors to consider in this regard:
- Data lineage tracking and data cataloging
- Regular data quality checks and validation processes
- Investing in data quality management tools and platforms
- Fostering a culture of data quality awareness and accountability
Implementing these practices will help reduce the likelihood of data errors, inconsistencies, and corruption, ultimately contributing to the success of your CDC replication implementation.
Monitoring & Handling Errors
To minimize the impact of errors, establish a comprehensive monitoring and alerting system that provides real-time visibility into the performance and health of your CDC Replication process.
This enables your team to quickly identify and resolve issues, preventing them from escalating into more significant problems.
Consider the following practices for monitoring and handling errors:
- Set up real-time monitoring and alert systems
- Establish a comprehensive error-handling strategy
- Equip your team to handle error scenarios through training, documentation, and access to appropriate tools and resources
In addition to these practices, fostering a culture of proactive problem-solving and continuous improvement can help your team anticipate potential issues and develop robust solutions. This collaborative approach can lead to a more resilient and efficient CDC Replication process.
Handling Schema Changes
Effective schema change management is necessary for maintaining a seamless CDC replication process. Schema changes can significantly impact the CDC replication process, potentially leading to data corruption, inconsistencies, and system failures if not properly managed.
To manage schema changes, consider the following strategies:
- Automate schema change detection and adaptation, whenever possible
- Invest in CDC replication solutions designed to handle schema changes
- Develop, document, and communicate robust procedures for implementing schema modifications
Implementing these strategies will help ensure that your CDC replication process remains resilient and adaptable in the face of evolving data structures and requirements.
Optimizing Performance
To optimize the performance of your CDC replication process, regularly assess your system's performance and implement performance-tuning measures. This helps ensure that your CDC replication process remains efficient and effective, enabling your organization to derive maximum value from its data assets.
Practices for optimizing performance include:
- Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) like throughput, latency, and resource utilization
- Implementing performance tuning measures, such as indexing, partitioning, and parallel processing
- Continuously iterating and refining your CDC replication implementation to adapt to changing business needs and technological advancements
Conclusion
CDC replication is a crucial part of modern data architectures. By understanding the various CDC replication approaches, use cases, and best practices, organizations can utilize the full potential of their data and drive informed decision-making.
When you start on your CDC replication journey, having the right tool can make all the difference. At Estuary, we developed Flow to provide a comprehensive solution for CDC that can adapt to the unique requirements of your organization. This makes Flow an excellent choice for those trying to modernize their data infrastructure.
So if you are ready to reap the benefits of the CDC and elevate your data strategy, sign up to try Flow for free and start exploring its extensive features.

Author
Popular Articles